Lost Wonder of the World: The Library of Alexandria

Lost Wonder of the World: The Library of Alexandria
Welcome to a trip back in time to explore the lost wonder of the world, the Library of Alexandria. This ancient treasure held an incredible wealth of knowledge and played a significant role in shaping human history. Let's uncover the significance of this grand establishment and delve into the mystery surrounding its demise.
The Significance of the Library of Alexandria
The Library of Alexandria was more than just a collection of books; it symbolised human intellect and curiosity. Established in the 3rd century BC, it became the epicentre of ancient scholarship, attracting scholars, philosophers, and scientists from all corners of the world. The library housed an estimated 400,000 to 700,000 scrolls, making it the most extensive library of its time. It offered various writings on various subjects, including philosophy, mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and literature.
This extraordinary institution became a beacon of knowledge, fostering intellectual discourse and pushing the boundaries of human understanding. Scholars gathered here to exchange ideas, research, and make groundbreaking discoveries. The library was not only a place of learning but also a catalyst for innovation and cultural exchange.
The Mystery Surrounding Its Destruction
The destruction of the Library of Alexandria remains one of history's greatest mysteries. While there are multiple theories, pinpointing the exact cause is challenging due to the lack of concrete evidence. One widely debated theory suggests that the library suffered from multiple incidents of destruction rather than a single catastrophic event.
Scholars attribute its demise to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 BC, where Julius Caesar's army accidentally set fire to the library during the Siege of Alexandria. Another theory proposes that the library fell victim to various fires and political turmoil over the centuries. Religious conflicts during the rise of Christianity and the subsequent invasion by Arab forces are also believed to have contributed to its ultimate destruction.
The destruction of the Library of Alexandria was undoubtedly a great loss to humanity's collective knowledge. Countless irreplaceable manuscripts vanished forever, leaving gaps in our understanding of ancient civilizations and their advancements.
While the Library of Alexandria may be lost to the ages, its legacy remains a symbol of the pursuit of knowledge and the perils that can befall even the greatest treasures. It serves as a reminder of the importance of preserving and valuing our intellectual heritage for future generations.

Lost Wonder of the World: The Library of Alexandria
History of the Library of Alexandria
Welcome to a trip back in time to explore the lost wonder of the world, the Library of Alexandria. This ancient treasure held an incredible wealth of knowledge and played a significant role in shaping human history. Let's delve into the intriguing history of this grand establishment and discover its remarkable contributions.
Founding of the Library by Ptolemy I
The Library of Alexandria was founded in the 3rd century BC by Ptolemy I, one of Alexander the Great's generals who became the ruler of Egypt. Recognizing the importance of knowledge, Ptolemy I established the library as a centre for intellectual excellence. He envisioned a place where scholars from all over the world could gather, exchange ideas, and contribute to advancing knowledge.
Contributions and expansion under Ptolemy II
Under the reign of Ptolemy II, the Library of Alexandria experienced its golden age. Ptolemy II recognized the significance of expanding the library's collection and attracting renowned scholars from various disciplines.
The library became a thriving hub of intellectual activity, boasting an estimated 400,000 to 700,000 scrolls. It housed many writings, including works on philosophy, mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and literature. Scholars flocked to the library to conduct research and engage in profound intellectual discussions, making groundbreaking discoveries in their respective fields.
Ptolemy II also placed a strong emphasis on preserving all written works brought to Alexandria. Ships entering the port of Alexandria were required to surrender any books they carried, allowing the collection to expand continuously.
The library's influence extended far beyond Egypt, attracting the brightest minds of the time. It facilitated cultural exchange and sparked innovation by fostering collaboration among scholars from diverse backgrounds.
Sadly, the Library of Alexandria fell victim to many destructions and fires over the centuries. The exact cause remains a mystery, with theories ranging from accidental fires during military conflicts to deliberate destructions during religious and political upheavals.
While the physical library may be lost, its legacy inspires generations. The Library of Alexandria serves as a poignant reminder of the importance of preserving and valuing knowledge, as well as the enduring power of intellectual pursuits.
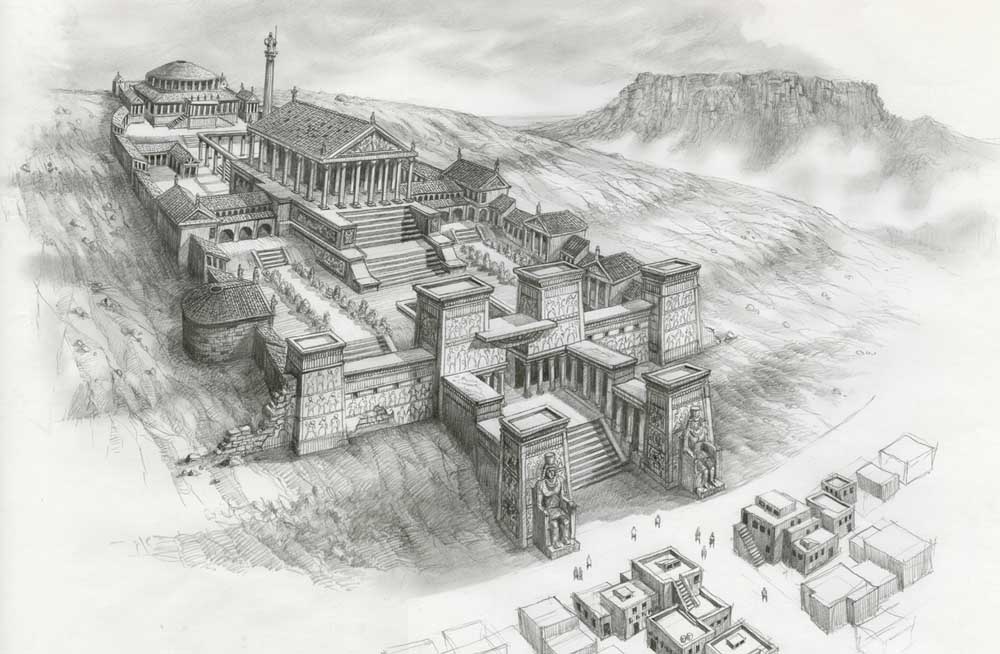
Lost Wonder of the World: The Library of Alexandria
Architecture and Design
Welcome to the architectural marvel that was the Library of Alexandria. Prepare to be awestruck by its grandeur and scale as we delve into the fascinating details of its design.
The grandeur and scale of the Library
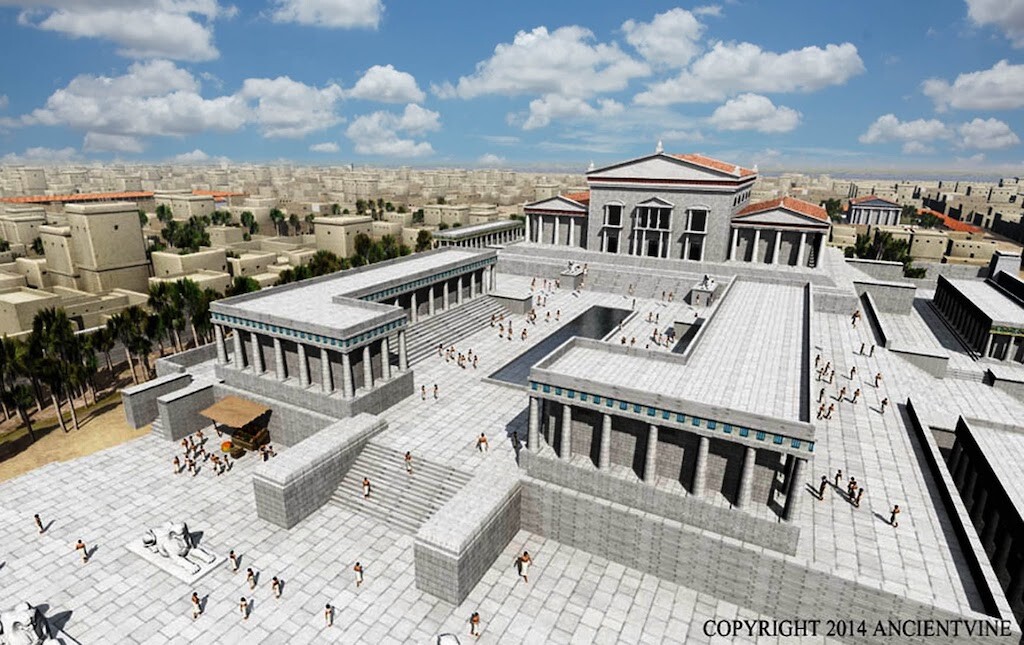
The Library of Alexandria was a testament to the magnificence of ancient architecture. Situated in the heart of Alexandria, Egypt, it was a massive structure that stood as a symbol of knowledge and intellectual excellence. With its sprawling complex and impressive façade, the library commanded attention and drew scholars and visitors from all over the world.
The exact dimensions of the Library of Alexandria are not known, but historical accounts suggest that it was a vast structure with multiple buildings, courtyards, and gardens. Its construction combined elements of Greek and Egyptian architecture, creating a unique blend of styles that reflected the cultural fusion of the time.
The library's exterior was adorned with intricate carvings and sculptures, showcasing the artistic mastery of the craftsmen involved. Marble columns lined the entrance, creating a sense of grandeur and welcoming visitors into a world of knowledge and discovery.
The layout and organization of the library's collections
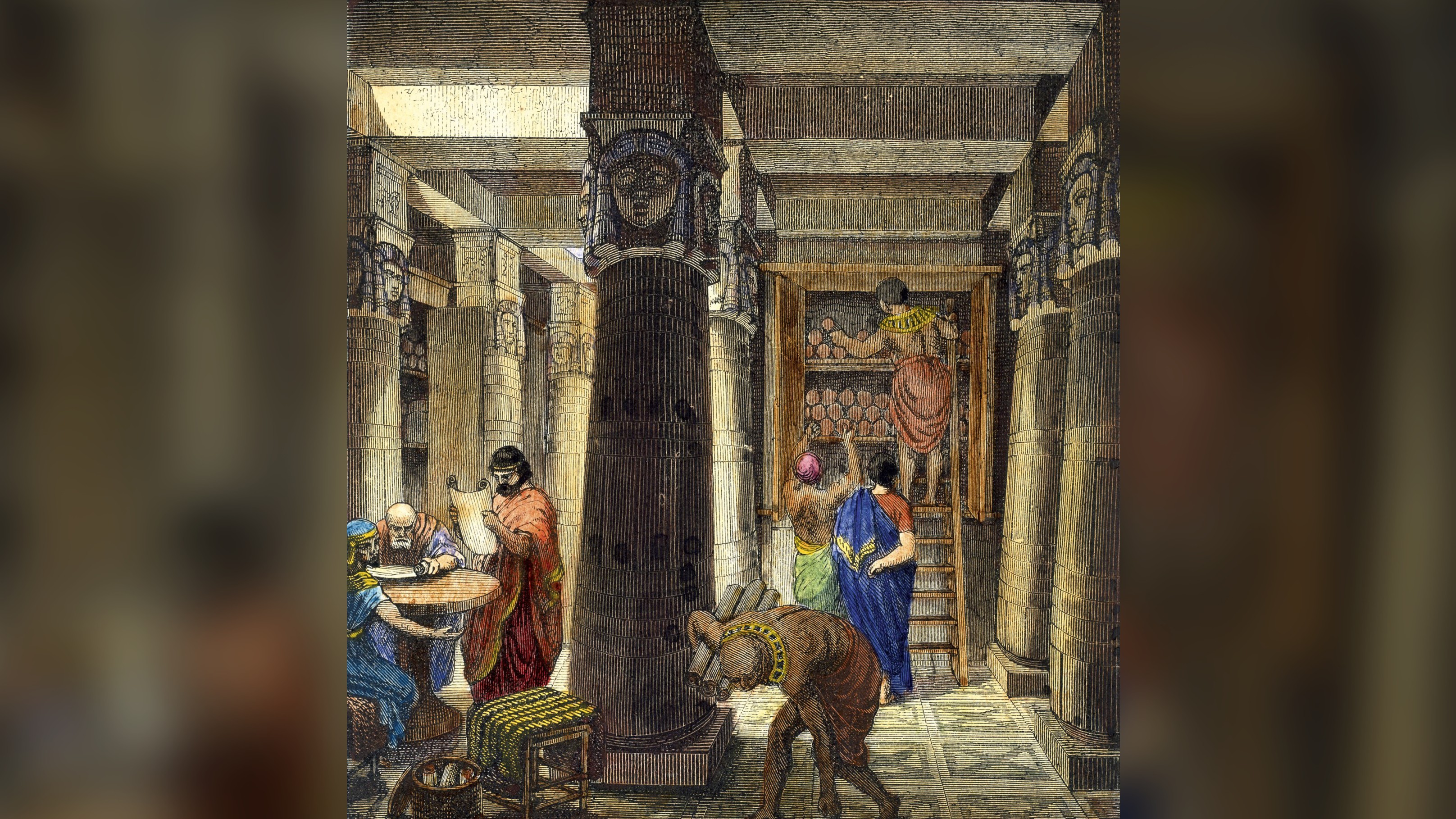
Inside the Library of Alexandria, the organization and layout of the collections were equally impressive. The library housed many scrolls and books, meticulously organized and categorized for easy access.
Scholars and librarians employed a sophisticated system to keep track of the vast collection. Each scroll or book was assigned a unique identifier, and shelves were meticulously labelled to ensure quick retrieval. Various sections were dedicated to disciplines, including philosophy, mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and literature.
The library also boasted lecture halls and study rooms, creating a thriving intellectual environment. Scholars could engage in discussions, attend lectures, and collaborate on research projects, fostering innovation and knowledge-sharing.
Unfortunately, the Library of Alexandria met a tragic fate, with fires and destruction over the centuries wiping out this magnificent institution. While its physical presence may be lost to history, its legacy lives on, a testament to the human thirst for knowledge and the enduring power of intellectual pursuits.
The Library of Alexandria was not only a remarkable architectural feat but also a beacon of knowledge that attracted scholars and thinkers from around the world. Its grandeur and meticulously organized collections made it a centre of intellectual excellence and inspiration. Although it may be a lost wonder of the ancient world, its impact continues to be felt in how we value and preserve knowledge today.

Collection and Contents
Scholars and works housed in the Library
The Library of Alexandria was a treasure trove of knowledge, housing the works of many esteemed scholars of the time. It attracted renowned intellectuals, philosophers, and poets who sought to expand their understanding of the world. Some of the most notable scholars whose works were preserved in the library included Plato, Aristotle, Socrates, Euclid, Hippocrates, and Archimedes. These brilliant minds contributed groundbreaking theories, philosophies, and discoveries that have shaped the world we know today.
The library also acted as a gathering place for scholars from different cultures and backgrounds. It facilitated the exchange of ideas and fostered discussions that sparked intellectual growth. It was a melting pot of diverse perspectives and ideologies where thinkers of different disciplines could collaborate and challenge each other's ideas.
Languages and subjects represented in the collection
The collection within the Library of Alexandria was extensive and encompassed a wide range of subjects. It consisted of texts written in various languages, including Greek, Latin, Egyptian, Persian, and Hebrew. By including works written in multiple languages, the library aimed to preserve knowledge from different cultures and ensure accessibility to a broader audience.
Subjects covered in the library's collection spanned multiple disciplines, including philosophy, mathematics, astronomy, medicine, literature, history, and geography. The vast array of subjects reflected the library's commitment to preserving and disseminating knowledge across diverse fields.
The library's curated collection served as a valuable resource for scholars and students, offering a comprehensive foundation for intellectual exploration and research. The availability of such a diverse range of works created an environment where individuals could deepen their understanding and contribute to advancing knowledge.
The Library of Alexandria housed the works of renowned scholars and intellectuals from various cultures and languages. Its collection spanned various subjects, promoting interdisciplinary learning and fostering intellectual exchange. The library played a vital role in preserving and disseminating knowledge, creating a hub of intellectual excellence that continues to inspire and captivate the imagination of scholars and historians today.
Destruction of the Library
The Burning of the Library during the Roman Conquest
The Library of Alexandria, often called the Lost Wonder of the World, met its tragic demise during the Roman conquest of Egypt. The exact details of the library's destruction remain a subject of debate and speculation, but it is widely believed that a significant portion of its vast collection was lost forever.
As the Roman Empire expanded, Julius Caesar's troops arrived in Alexandria in 48 BCE. It is said that during the Siege of Alexandria, a fire broke out in the city, and some sources suggest that the library caught fire accidentally. However, other accounts claim that the Roman army intentionally set fire to the library as an act of war.
The burning of the Library of Alexandria has been a source of great sorrow and frustration for scholars and historians. The loss of countless manuscripts, scrolls, and works of art was a devastating blow to the accumulated knowledge and intellectual heritage of humanity.
Debates and Theories about the Extent of the Destruction
The exact scale of the destruction and the number of works lost in the fire continue to be debated among scholars. Some estimates suggest that the library contained hundreds of thousands of scrolls, while others propose that the number may have reached the millions. Nevertheless, even a single work from that esteemed collection is a loss to the world.
There is also ongoing debate regarding the scope of the library's destruction. Some historians argue that subsequent fires and invasions, including the Arab conquest of Egypt in the 7th century, contributed to the gradual deterioration and ultimate disappearance of the library. Others believe that a substantial part was preserved or copied before its destruction. While the truth remains elusive, the mere thought of the vast knowledge potentially lost to humanity leaves us with a profound regret.
The burning of the Library of Alexandria remains a powerful reminder of the impermanence of knowledge and serves as a cautionary tale about the consequences of losing historical treasures. It emphasizes the importance of preserving and protecting our cultural heritage, as well as the need to continue the pursuit of knowledge to build a brighter future.

Legacy and Influence
The impact of the Library on ancient knowledge
The Library of Alexandria, often referred to as the Lost Wonder of the World held a central role in the preservation and advancement of ancient knowledge. It was a beacon of intellectual and cultural activity, attracting scholars from all corners of the ancient world. The loss of this magnificent institution was a tragic blow to humanity's accumulated knowledge, and the legacy it left behind is profound.
The Library housed a vast collection of manuscripts, scrolls, and works of art from various civilizations. It became the centre for research, where scholars could study and translate texts from different cultures. As a result, it played a significant role in exchanging ideas, fostering intellectual curiosity, and pushing the boundaries of knowledge in fields such as mathematics, astronomy, medicine, philosophy, and literature.
The destruction of the Library, whether accidental or intentional, was a catastrophic event. It led to the loss of countless works that could have provided invaluable insights into ancient civilizations and their contributions to human history. The absence of these texts continues to leave gaps in our understanding of the past.
Efforts and attempts to restore or replicate the Library
Throughout history, there have been various efforts and attempts to restore or replicate the Library of Alexandria. Modern scholars and enthusiasts have recognized its historical significance and the need to honour its legacy.
The Bibliotheca Alexandrina, inaugurated in 2002, is a testament to these efforts. Located near the site of the original Library, it aims to recreate the spirit of the ancient institution. It houses millions of books, hosts cultural events, fosters research, and promotes dialogue among different cultures.
Furthermore, digitization initiatives have allowed access to ancient texts and resources, making them available to a global audience. Online repositories and digital libraries have enabled researchers and scholars to explore and study ancient manuscripts that were previously inaccessible.
While these attempts to restore or replicate the Library may never fully recreate its breadth and depth, they act as a tribute to the enduring legacy of the Library of Alexandria.
The Library of Alexandria's impact on ancient knowledge cannot be overstated. Its tragic destruction deprived humanity of an invaluable treasure trove of wisdom and insight. However, efforts to restore its influence and preserve its memory continue to shape the pursuit of knowledge and inspire generations to honour the past while forging a brighter future.

Rediscovery and Excavation
Historical accounts and records of the Library's location
The Library of Alexandria considered the Lost Wonder of the World, stood as a symbol of intellectual and cultural excellence in ancient times. For centuries, its actual location remained a mystery, as the once grand structure was reduced to ruins. However, historical accounts and records provided clues about its possible whereabouts.
Ancient texts mentioned that the Library was near the Great Harbor of Alexandria, on the northeastern tip of Egypt. These records also indicated it was near the Royal Quarter and the famous lighthouse, Pharos. With this information, archaeologists and historians embarked on a mission to rediscover this lost treasure.
Excavation efforts and discoveries at the site
Excavation efforts in the late 19th and early 20th centuries led to significant discoveries at the site believed to be the location of the Library of Alexandria. Archaeologists uncovered remnants of buildings, archaeological artefacts, and scrolls that provided invaluable insights into the past.
One of the most notable discoveries was the Serapeum, a temple dedicated to the god Serapis, which also housed a library. This finding shed light on multiple libraries within the ancient city.
Additionally, excavations revealed underground tunnels and passageways likely used to transport books and manuscripts between different buildings. These findings suggested a complex network of interconnected libraries throughout the city.
Although the exact extent of the Library's physical structure remains unknown, the excavations unearthed evidence of its existence and the cultural significance it held during its heyday.
The Lost Wonder of the World, the Library of Alexandria, has captivated the imaginations of historians and archaeologists for centuries. Through historical accounts and dedicated excavation efforts, we have been able to rediscover important clues about its location and gain insights into its grandeur. While the physical structure may have been lost to time, the legacy and intellectual impact of
